Mitigating Cloud Risks: Simple Steps to Prevent Incidents
Background:
Based on well-known practices and yearly reviews over the infosec industry channels, a significant part of incidents occurring in the cloud are primarily caused by misconfigurations of the assets themselves. This indicates that the threat landscape has shifted over the years from highly sophisticated attacks to less sophisticated ones, where anyone can exploit the weaknesses of the environment. This change is partly because cloud providers have already taken care of the system and lower-level challenges that usually require interaction from senior-level specialists. As a cloud consumer, you only need to take care of your infrastructure architecture and perform some basic level hardening to prevent exploitation of your environment. In this article, I will provide a high-level overview of how to use two components to address such gaps.
Key Elements To Resolve Challenge:
- CIS cloud benchmark
- Scripting capability
CIS cloud benchmark component :
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) releases numerous papers related to system hardening, which are applicable to cloud environments and various operating systems. To begin, you need to choose the scope or vendor you're interested in—in our case, we’ll focus on AWS or Azure.
After opening the relevant CIS Benchmark document, you'll find multiple sections. Once you've selected a specific section, you'll be able to view the recommended configurations along with the audit or checking methods used to verify compliance.
For our example, let's choose "Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one uppercase letter (Scored)." Based on the paper, it is suggested to run the "aws iam get-account-password-policy" command over the CLI.

Now open the official AWS documentation and review the possible values returned by the AWS infrastructure when making a request to their API using the CLI.
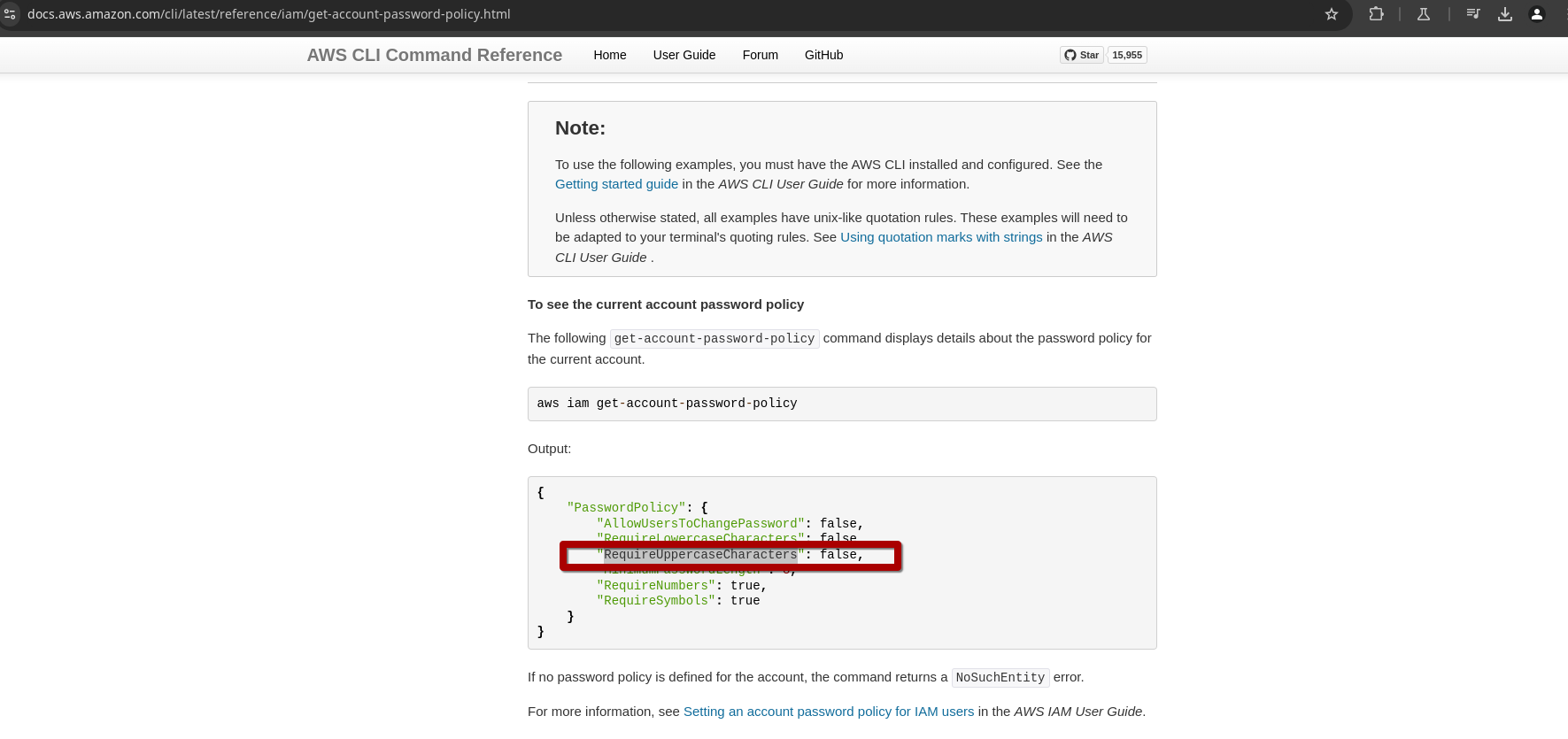
From the top screenshot, you can see that AWS shows that configuration in their response and returns the key named "RequireUppercaseCharacters," which is assigned a Boolean type.
Scripting :
Now let's combine our knowledge about CIS and AWS into a technical implementation.
- Create the desired scope/configuration with which you want to interact using a flowchart.
- Predefine system calls to the service and correlate them with responses returned by the noted cloud provider using a flowchart.
- Create a system account at the root level with reader permissions.
- Implement your flowchart into technical chunk of code
Conclusion:
This approach does not solve all the challenges associated with the attack landscape against the cloud. However, in the early stages, it can help ensure that basic misconfigurations will not be the root cause of your infrastructure compromise.
Stay Safe ! j0ker
