Agentic AI challenges in IDE: Forensic and extraction of traces PART 1
Background: With the rise of AI companions and agentic features in popular IDEs, these tools can now execute commands with user consent. This presents new challenges for digital forensic specialists, who must analyze IDE-level activity on compromised machines. Malware may also target sensitive data stored in IDE cache locations. I aim to research forensic processes related to agentic AI in IDEs, focusing on identifying new types of historical logs that can aid digital investigations. As a first step, we will target the VSCode environment.
Traces for VSCODE:
During my research, I activated Sysmon on a Windows machine and instructed an agentic AI to create a file in a specific directory. The Sysmon logs showed that only one component, vscode.exe, was responsible for creating the file. This means that when analyzing Sysmon logs, you should always include the "Image" field and search for all activities involving "code.exe" to trace relevant actions performed by the IDE.
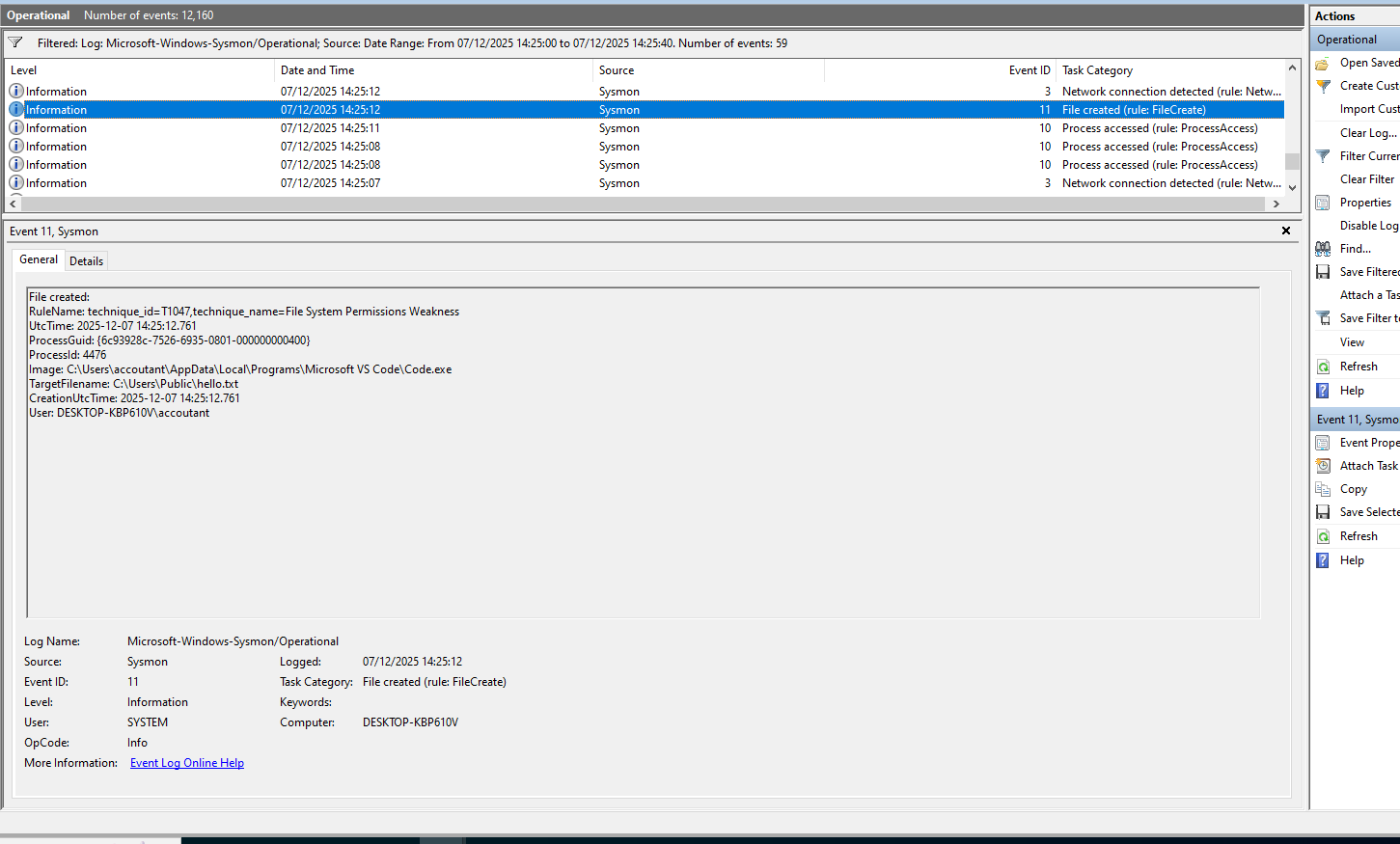
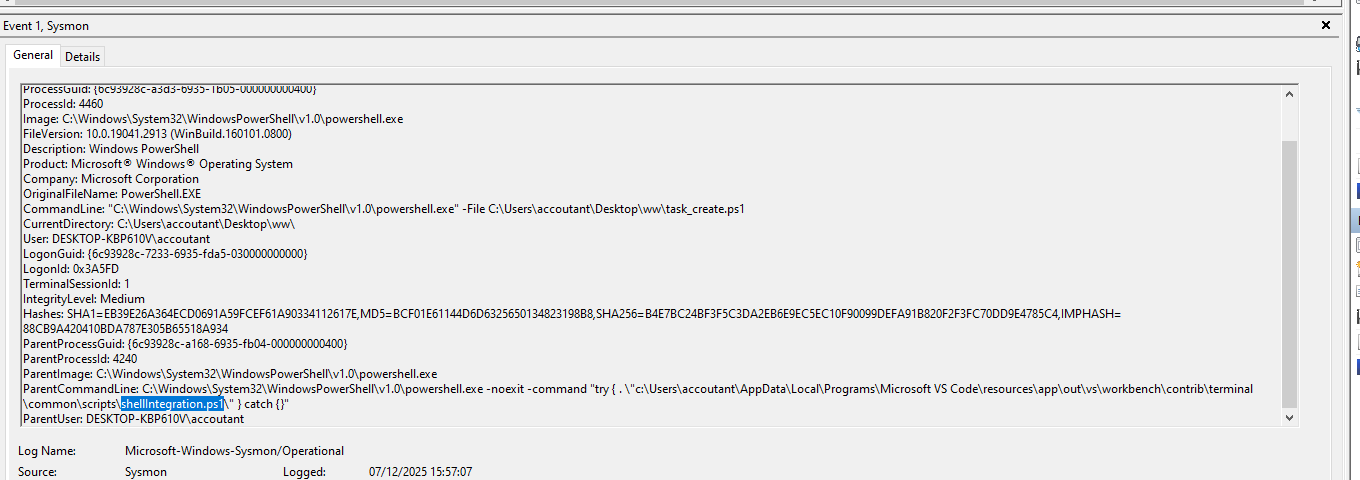
In another experiment, I instructed an agentic AI to create a new scheduled task, which was executed via PowerShell created file. In all cases where PowerShell was run, the Sysmon logs consistently showed that the ParentCommandLine field contained the string "shellIntegration.ps1." This indicates a static component is present whenever agentic AI triggers PowerShell through VSCode, making "shellIntegration.ps1" a useful artifact to search for during forensic analysis.
Extract logs from VSCODE:
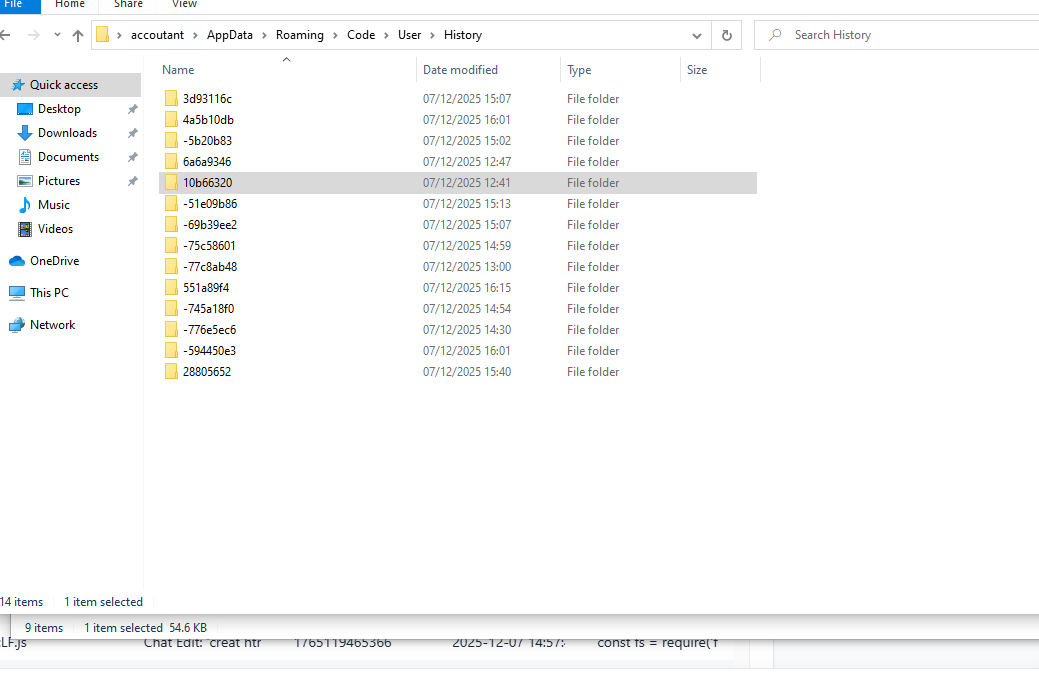
During the research, it was discovered that user history, including request times and created files, is stored in the temp folder at C:\Users\YourUserName\AppData\Roaming\Code\User\History. This means we can create a simple forensic script to retrieve all artifacts from this location.
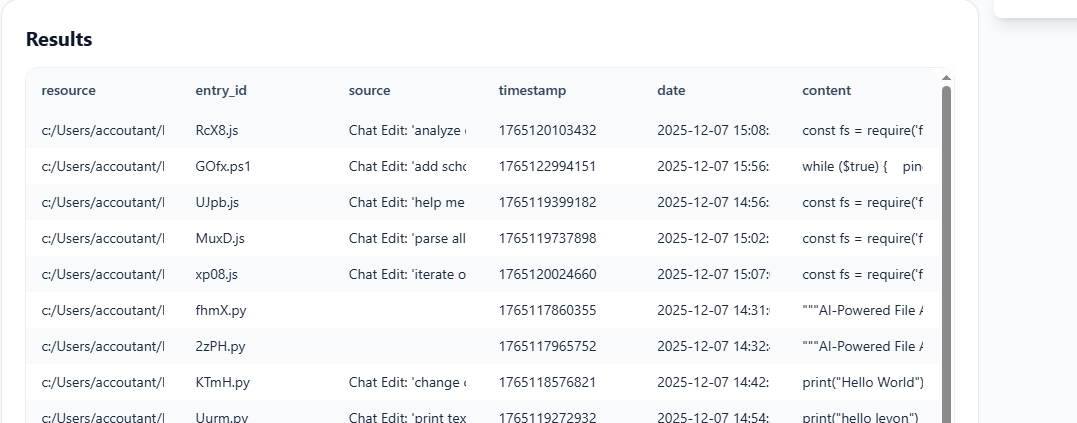
Conclusion: This research should continue to keep pace with emerging technologies, ensuring effective response in urgent incident cases.
